Mastering Treasury Reconciliation: Understanding the Payment Lifecycle
No one can argue that efficient and secure payment processes are absolutely crucial for smooth operations and robust financial management.
A fundamental understanding of the payment lifecycle, the series of stages a payment goes through from initiation to reconciliation, empowers businesses to optimise their financial processes, reduce errors, and enhance security.
Here is an overview of each key phase of the payment lifecycle and strategies for managing these stages effectively to achieve business efficiency and security.
1. Payment Initiation
This phase involves the creation and authorisation of a payment. Whether it's through wire transfers, ACH, credit card, or other methods, ensuring a smooth initiation process is essential for a seamless payment lifecycle.
Challenge: Manual errors, missing authorisations, and incomplete data can cause delays and errors during initiation.
Best Practices:
• Automate Payment Creation: Implement automated tools to create payments with minimal manual input, reducing errors and improving speed.
• Establish Approval Workflows: Set clear approval workflows with multiple levels of authorisation to prevent unauthorised transactions and enhance security.
• Centralise Payment Requests: Consolidate payment requests from various departments in a single system to improve control and visibility.
2. Payment Processing
Once a payment is initiated, it moves through processing, where the financial institution verifies the details and, if validated, proceeds with the transfer of funds.
Processing times vary by payment type and institution, which can impact cash flow and overall efficiency.
Challenge: Delays in processing or transaction holds due to validation issues can disrupt cash flow and create operational inefficiencies.
Best Practices:
• Standardise Payment Method: Opt for standardised, reliable payment methods that align with your business needs and reduce complexity.
• Monitor Transaction Status: Use real-time monitoring tools to track the progress of transactions, enabling proactive management of potential delays.
• Maintain Updated Bank Information: Ensuring all account information is up to date reduces the risk of processing delays due to validation issues.
3. Payment Settlement:
Settlement occurs when the funds are successfully transferred from the payer’s account to the recipient’s account. This phase is crucial for timely and accurate cash management.
Challenge: Reconciliation issues and currency fluctuations (in the case of cross-border payments) can complicate settlement.
Best Practices:
• Use Predictive Analytics: Predictive tools can forecast settlement timelines, allowing finance teams to anticipate cash flow more accurately.
• Implement Currency Management Tools: For international transactions, currency management solutions can help mitigate the risk of currency fluctuations.
• Reconcile in Real-Time: Integrate systems that allow for real-time reconciliation to avoid discrepancies and enhance cash management.
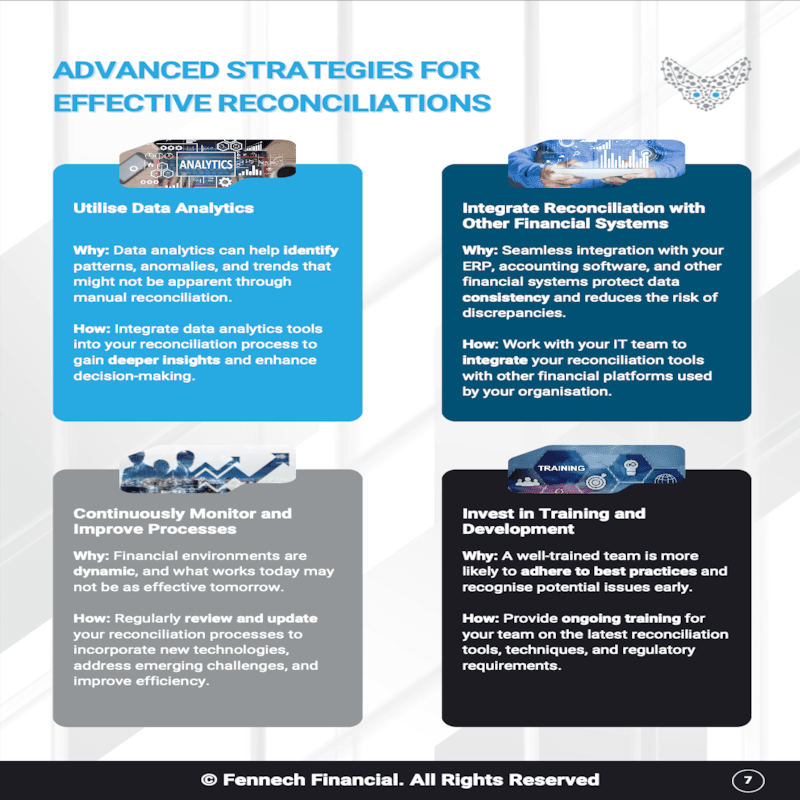
4. Payment Reconciliation:
Reconciliation involves comparing internal financial records with external bank statements to ensure all payments are correctly recorded and accounted for. This is one of the most time-consuming phases if managed manually.
Challenge: Manually matching transactions and resolving discrepancies is resource-intensive and prone to errors.
Best Practices:
• Automate Reconciliation: Automation tools can significantly reduce the time spent on reconciliation and improve accuracy.
• Centralise Financial Data: A centralised financial system simplifies reconciliation by consolidating records from multiple sources, making it easier to identify and resolve discrepancies.
• Establish Consistent Reconciliation Schedules: Conduct reconciliation regularly to catch errors early, improve reporting accuracy, and maintain financial health.